About Perovskite Solar Cells
Advantages of Perovskite Solar Cells

Technology from Japan! Four benefits
-
1
Originating in Japan
Utilizing Japanese technology and materials, efforts are combined in establishing mass production technology, creating demand, and setting up a production system. The Japanese government aims to achieve a power generation cost equivalent to silicon-based solar cells (14 yen/kWh) by 2030 and is aiming for early societal implementation.
-
2
Lightweight and Flexible
Compared to conventional solar panels, they are 1/100th the thickness and 1/10th the weight, making them thin and light. They are resistant to distortion and can be installed in places where conventional solar cells could not be.
-
3
High Conversion Efficiency
Already achieving an energy conversion efficiency comparable to conventional solar cells, research and development for practical application are ongoing.
-
4
Low Manufacturing Cost

Mass production is achieved through a manufacturing process that uses coating and printing technologies. As the material used is a thin film, less is required overall, resulting in a lower cost.
About Perovskite Solar Cells
About Solar Cells

Classification of Solar Cells
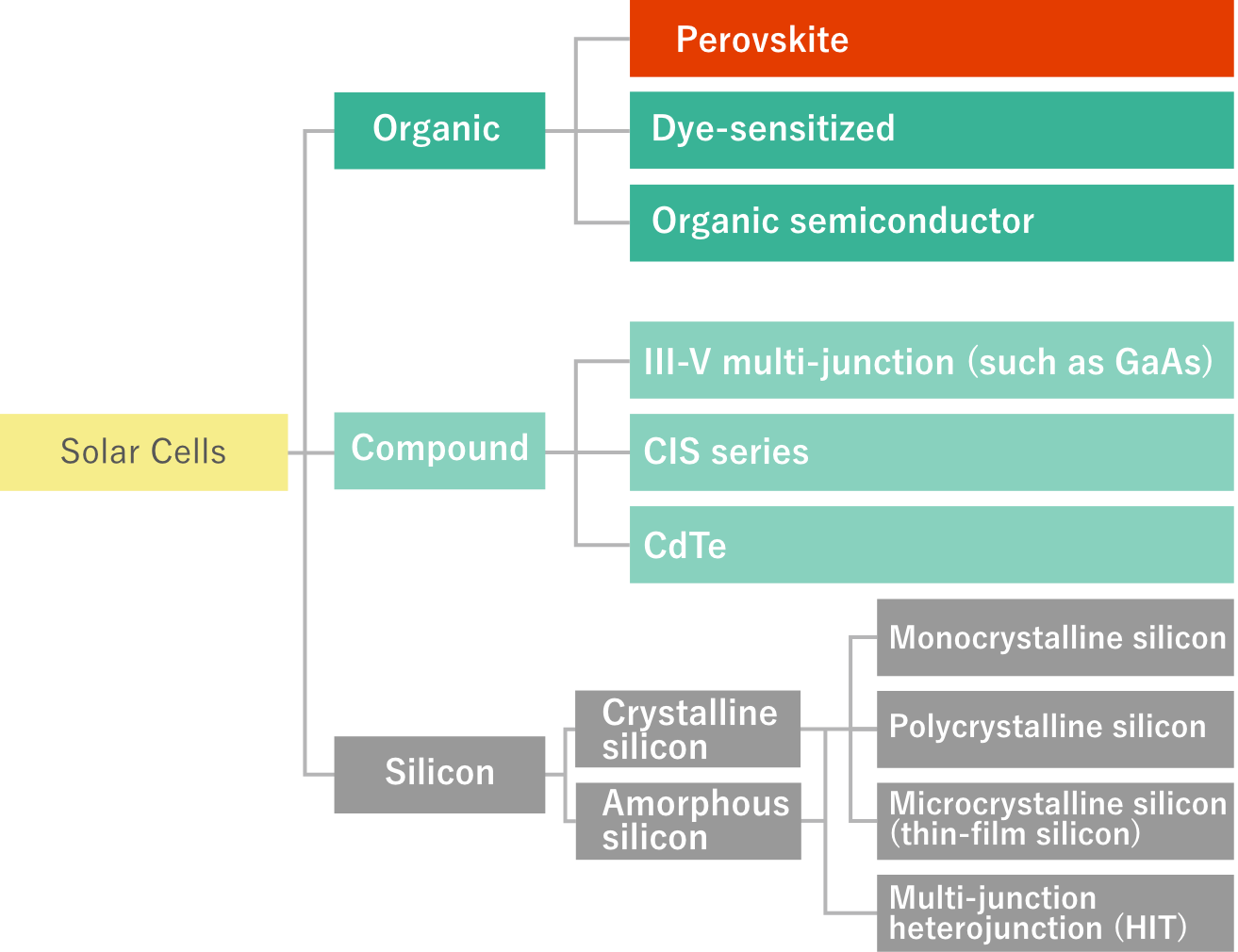
Solar cells range from low-cost to high-performance ones, from flexible to colorful varieties – their performance and form vary. They can be categorized based on the materials used inside. Broadly, they can be classified into three types: organic, compound, and silicon. Currently, 95% of the market consists of silicon-based solar cells. Rapid development over the last decade has been seen in "perovskite solar cells," which use a crystalline structure called perovskite – a technology originating from Japan.
Perovskite Structure
About Perovskite Solar Cells
Comparison with Silicon Solar Cells

Perovskite can generate power even indoors
Perovskite solar cells are lightweight and flexible solar cells that can be processed using coating techniques. They also have the characteristic of achieving high power generation efficiency even under low-light conditions, such as indoors, making them a promising new renewable energy technology widely usable in various devices and locations.
-
Perovskite
Solar CellsSilicon
Solar Cells -
Weight (example)
0.25kg/m2
22kg/m2
(including 7kg for the frame) -
Power generation efficiency (example)
26% (cell),
15% (module)14-20%
-
Power generation characteristics (low light conditions)
High power generation efficiency
Lower power generation efficiency
-
Shape
Lightweight & flexible
Heavy & rigid
-
Devices & Locations
High versatility
Limited versatility
-
Manufacturing cost
Low cost
High cost
-
Invention
2009
(starting in Japan)1950s
About Perovskite Solar Cells
Expected Proliferation in Cities

Looking forward to a "no charging" future
Due to their thinner, lighter, and more flexible characteristics compared to conventional solar cells, perovskite solar cells have the potential to dramatically increase installation locations. This includes areas previously challenging for installation, such as building walls and windows, cars, airplanes and drones, IoT sensors, smartphones, etc. Furthermore, local power generation and consumption using perovskite solar cells installed both outdoors and indoors in urban and rural areas are anticipated.
For the initiatives aimed at achieving carbon neutrality by 2050, solar power generation, which emits no CO2, is a promising option. Perovskite solar cells are expected to be the next-generation solar cells leading the transformation towards renewable energy as the primary power source for carbon-neutral solutions.




